Capturing of CO₂ (CCU/CCS)
The final step toward climate neutrality: capturing what we cannot avoid
Necessary plant engineering in cement plants and technology decisions
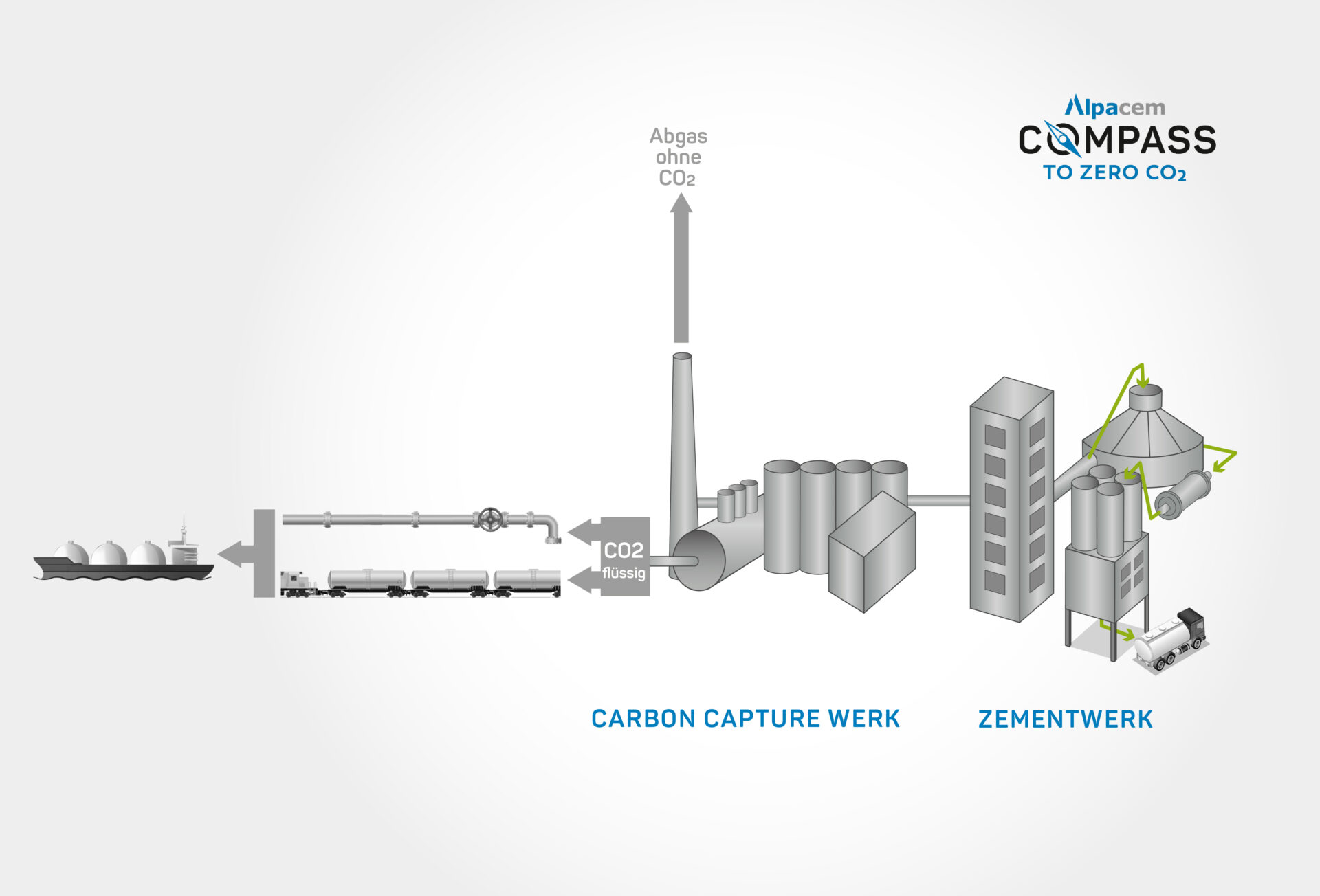
Even after all optimizations, there are still emissions that cannot be avoided. To prevent CO₂ from entering the atmosphere and thus achieve CO₂ neutrality, these residual emissions must be separated from the exhaust gas stream and either stored (CCS – carbon capture storage) or reused (CCU – carbon capture utilization). For cement plants that are fully integrated, this will be achieved by expanding and adapting the plant technology of the future and, depending on the separation technology, making changes to the existing plants.
These new technologies are currently under development, and we are examining various options for our cement plants. In doing so, we are facing challenges that must be solved step by step. These include:
- Technical challenges
- Investments and operating costs
- Legal and regulatory clarity
All these issues must be clarified in advance before implementation can take place.
We are preparing specifically for the future, building up internal expertise and implementation options for when the time is right.
Infrastructure requirements at our sites
- Electricity and energy requirements: All separation technologies will result in an increase in energy requirements
- Transport infrastructure: Transport options for the separated CO2 must be available
- Space requirements: Free space for plant development must be available
- Further requirements may arise from practical experience gained in the operation of pilot and test plants currently (2025) under construction
Storage and / or utilization of CO2
There are basically two conceivable value chains for captured CO2: on the one hand, it can be fed into downstream processes as a raw material to manufacture new usable products (CCU), and on the other hand, it can be transported to suitable geological storage sites and stored there safely and long-term (CCS).
Products manufactured using CCU must ensure that the CO2 is stored in the products for the long term. The list of products that comply with these rules is constantly being expanded. For example, CO2 can be incorporated into rocks and the resulting products can be reused in the construction industry. We are closely monitoring the legal framework for CCU in order to work with partners to develop possible new ways of storing our CO2 in the future.
Geological formations that offer space due to their porosity and sufficient impermeability due to overlying layers are suitable for long-term storage of CO2. This means that the greenhouse gas is no longer released into the atmosphere but is stored underground. Projects in Norway, for example, have been proving the safety of geological CO2 storage for several decades.
Legal Framework
The legal framework is not yet in place, but it is necessary in order to be able to carefully plan and make investments for the future. We are focusing on providing decision-makers in politics and the public sector with information about what we believe will be necessary framework conditions in the future.




